

Technology & Products
CycloneSEQ Sequencing TechnologyNanopore SequencingSequencing SoftwareReagentsFlow Cells
Application Scenarios
Application Fields
Service & Support
On-demand ServiceFAQ
About CycloneSEQ
About CycloneSEQStaff Development
Contact Us
Chinese (中文)English
Chinese (中文)English
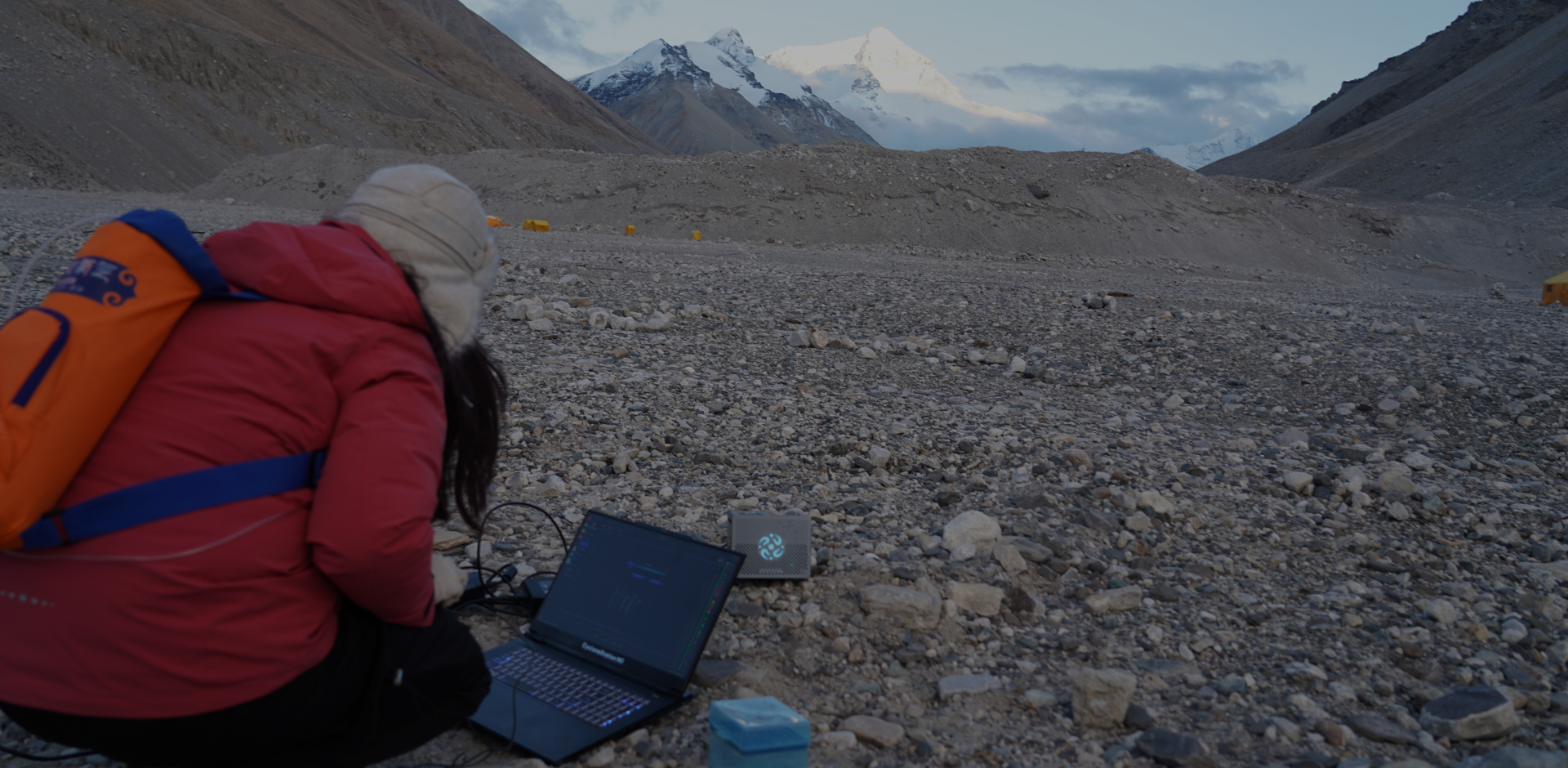




Penetrating the Mysteries of Life, Decoding Infinite PossibilitiesBreak the boundaries of life science research and application with independent innovation.
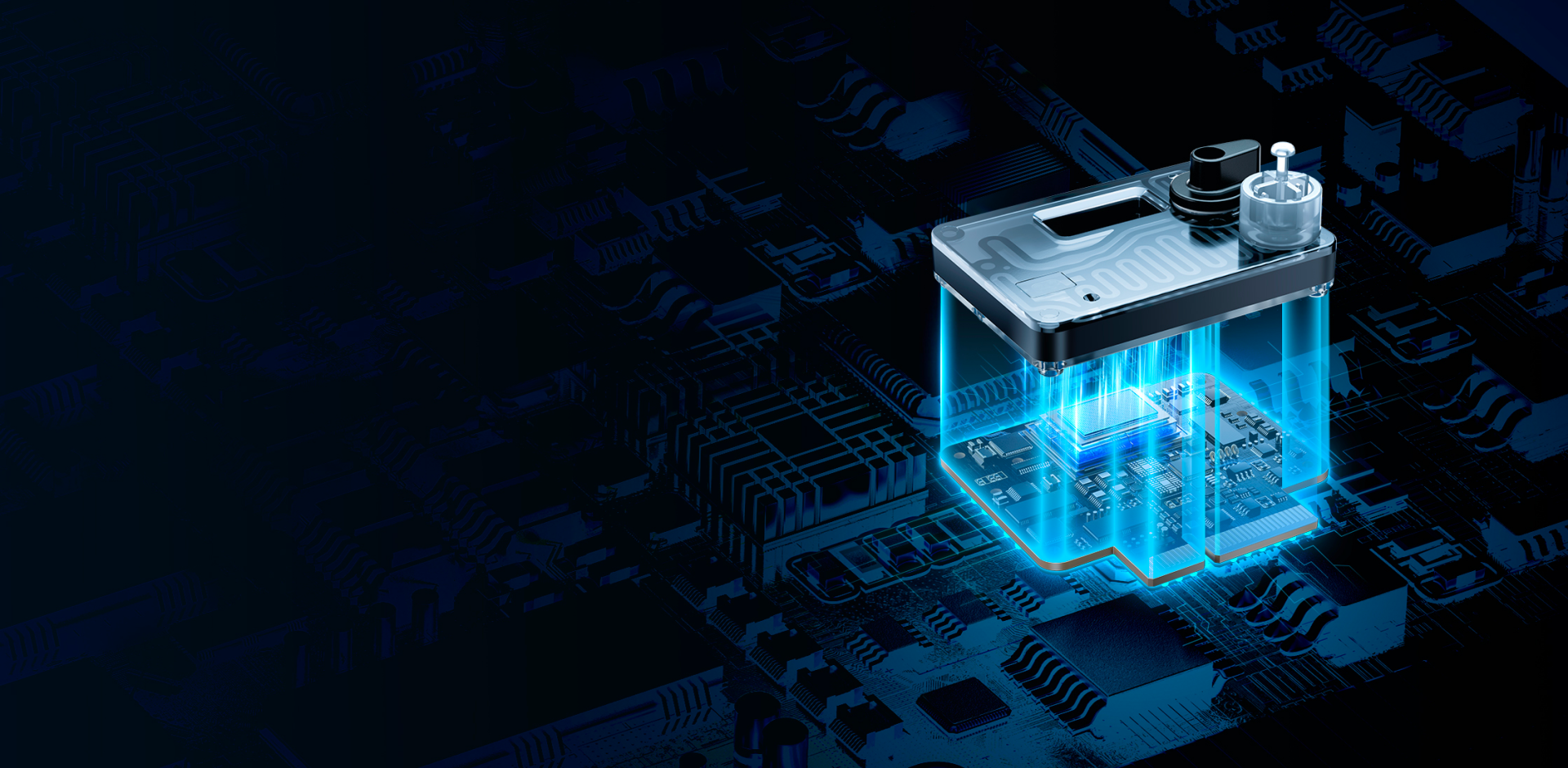
Integrated design featuring ASIC/MEMSEnlarged microcavities enabling ultra-long sequencing time
High-density array for pA-level current detection
High-density array for pA-level current detection
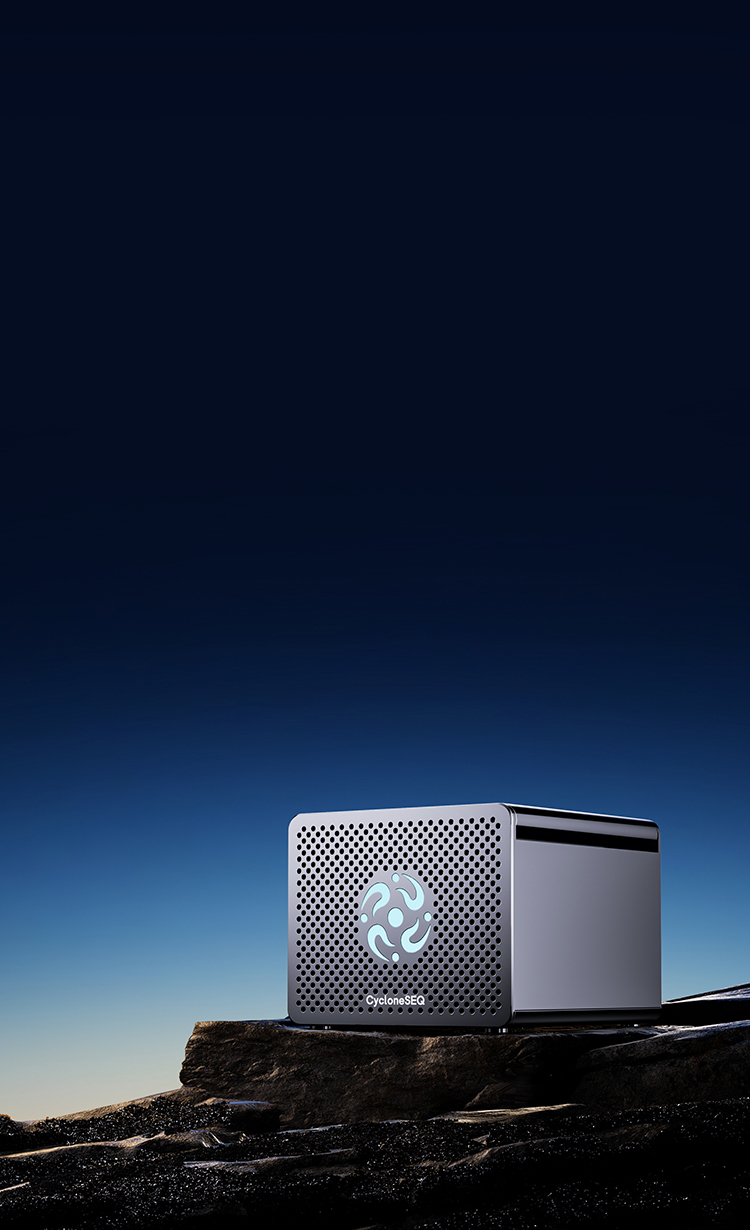


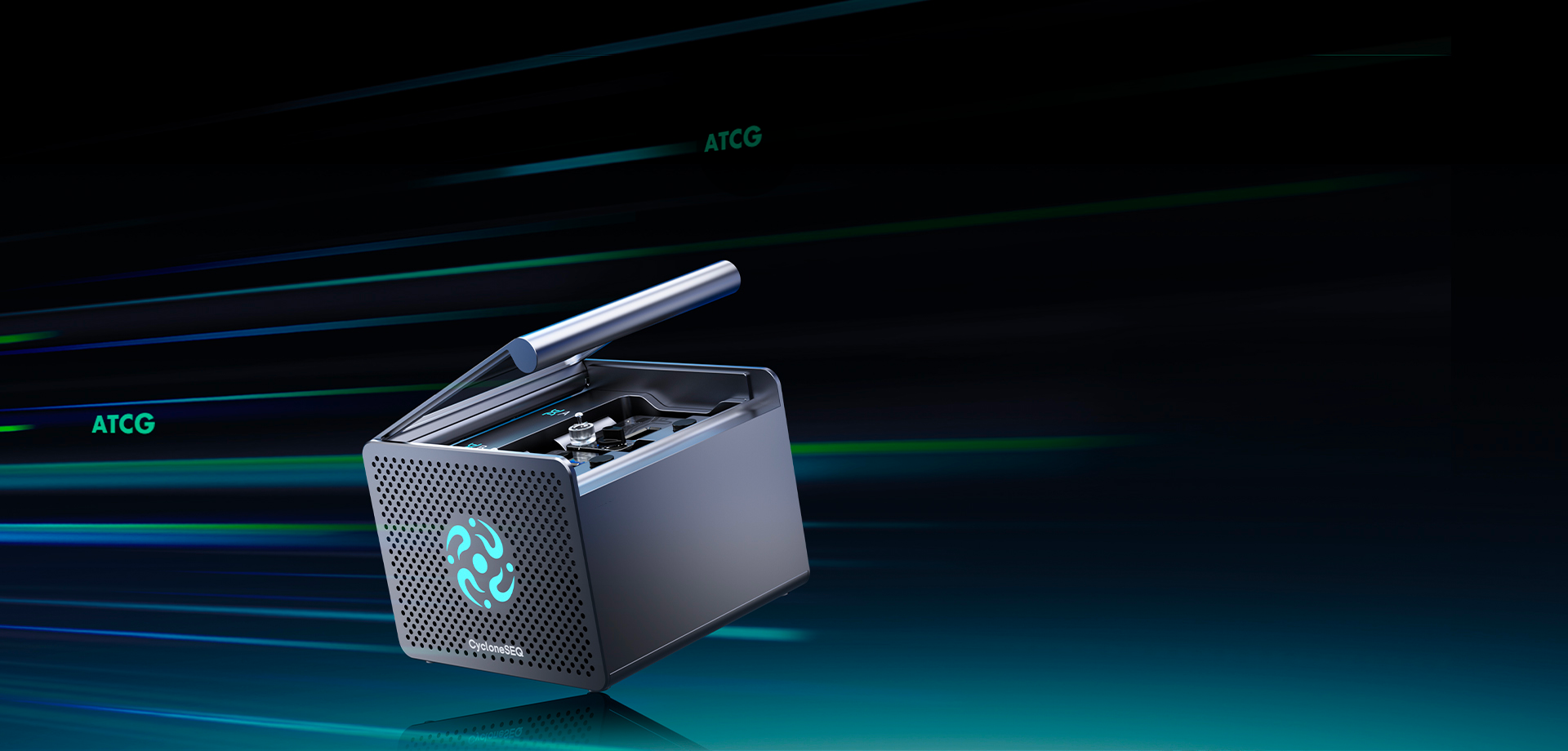
G100-ERNanopore Genetic SequencerNet Weight 3.08 kg165 mm (L) x 160 mm (W) x 127 mm (H)


Ultra-FlexibleDual-Flow Cell Innovation, Flexible Throughput OptionsRandom Access and Easy to Operate, Low Start-up CostReal-Time Acquisition of FASTQ Results

Ultra-FastRapid Library Preparation and ReadingReal-Time SequencingImmediate Output


Ultra-ComprehensiveBalanced for Both Short and Long ReadsEffortlessly Deciphers Entire GenomesComplete Genome Coverage
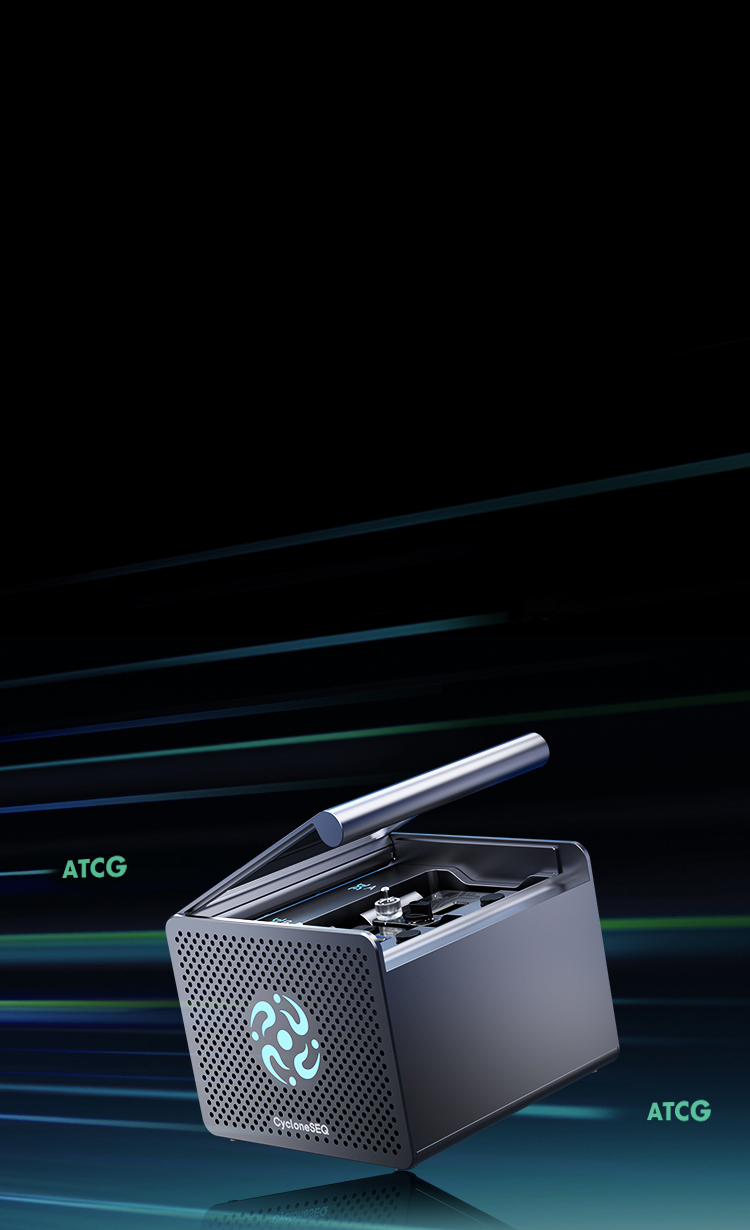


FastThe Charm of Speed
Sequencing Acquisition TimeReal-time
Number of Nanopore Proteins4096/Flow Cell
Designed Throughput / Flow Cell85 Gb
CycloneSEQ Sequencing Platform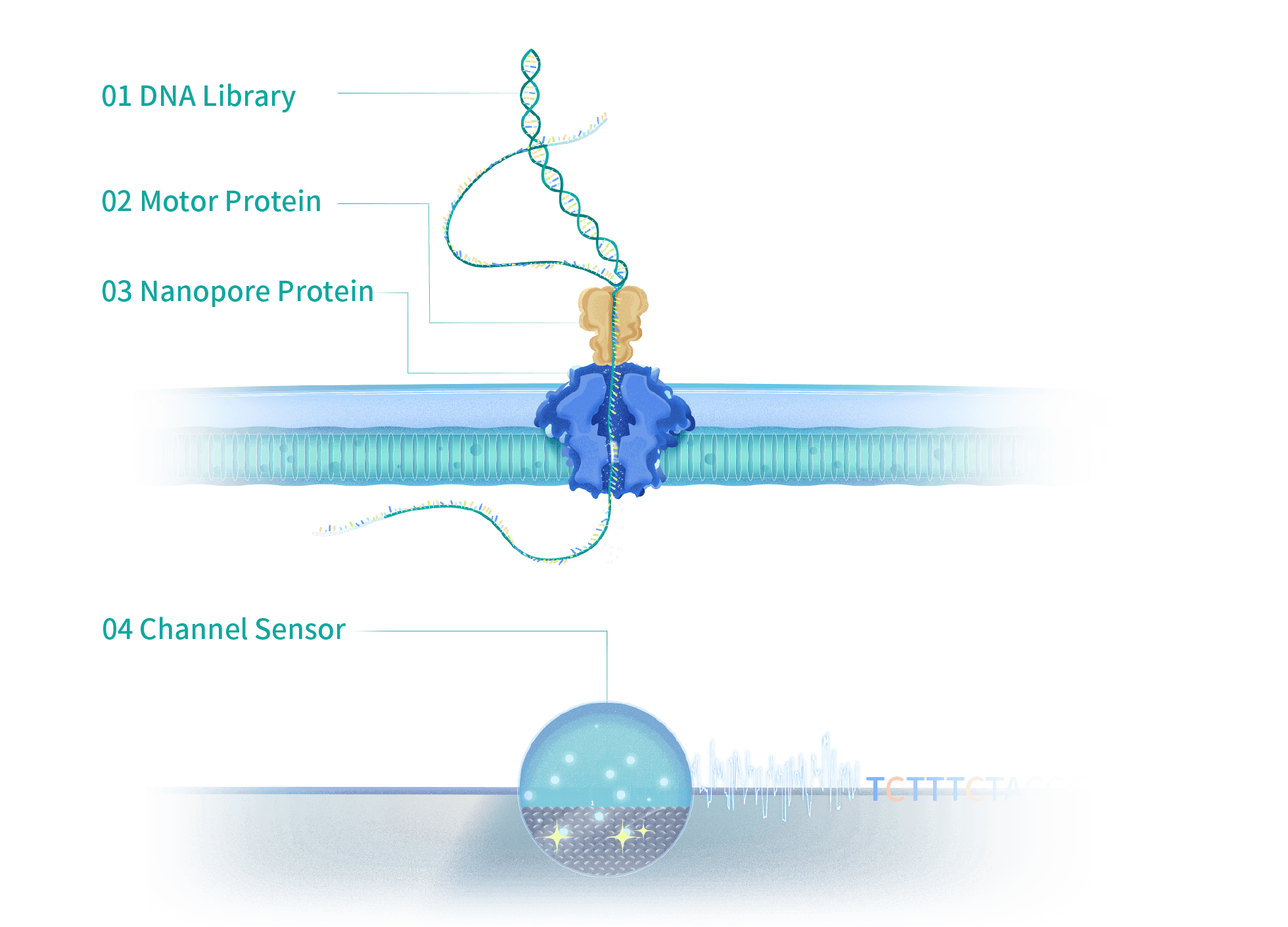

Technical Principle During sequencing on CycloneSEQ platform, DNA passes through nanopore proteins immobilized on a membrane in a single-stranded form, base by base, under the guidance of motor proteins. As different bases pass through the nanopore, changes in the ionic currents in the nanopore are triggered. These electrical signal changes are detected by channel sensors and decoded using a specialized base-recognition algorithm, enabling real-time and accurate determination of the base sequence on the DNA strand. The CycloneSEQ platform utilizes single-molecule nanopore chain sequencing technology. The DNA library molecules linked to the motor protein are drawn to the vicinity of the nanopore protein embedded in the membrane under the influence of electric field forces, where they are captured by the nanopore protein. Meanwhile, motor proteins situated near the nanopore proteins entrance, steadily and rapidly unwinding the DNA. This allows the DNA libraries to pass through the nanopore as a single strand. Different DNA bases and their arrangement impede the current to varying degrees, triggering the current fluctuations. The channel sensor captures these current fluctuation data and transmits them to the computer system, where basecalling algorithms parse the information to achieve real-time and accurate gene sequencing.
Core applicationsScientific Research >Clinical Practice >Emerging Fields >
GenomicsWith no GC bias, uniform coverage of highly repetitive regions, and no limitations on fragment read length, CycloneSEQ technology stands out as a valuable tool for genomic function and structural analysis. It can be used to resequence species with existing reference genomes, assemble genomes de novo, and resolve haplotypes, facilitating the uncovering of the functions of genomic "dark matter" and enhancing our insights into genomic complexity and diversity.
Single-cell SequencingTranscriptome analysis at the single-cell level enables the study of gene expression among different cell populations and plays a crucial role in cell heterogeneity research. CycloneSEQ can be used to sequence constructed single-cell full-length transcripts. This allows researchers to analyze transcript isoform diversity and gain more comprehensive cell information.
EpigenomicsEpigenetic modifications, such as DNA methylation, constitute an important dimension of genomic research and offer analysis value beyond the sequence itself. The CycloneSEQ team is actively developing direct detection methods for epigenetic modifications like methylation analysis. These methods, capable of providing multiple layers of information in a single sequencing run, promise to revolutionize epigenomics research.

Spatiotemporal OmicsSpatiotemporal omics allows obtaining cell type, molecular, and spatial location information at the same time, providing researchers with multidimensional avenues for analysis. In spatiotemporal omics research, CycloneSEQ provides more comprehensive transcriptome molecular information. Its application in areas such as immune repertoire analysis allows for a more profound understanding of how life functions and changes under varying temporal and spatial conditions.
TranscriptomicsBased on the analysis of full-length transcripts, CycloneSEQ can accurately identify both isoforms generated by alternative splicing and gene fusion events resulting from structural variations. With CycloneSEQ, achieving the sequencing length necessary for full-length transcript coverage is straightforward, eliminating the need for fragmentation. This results in a wealth of transcriptomic data, which holds significant importance in transcriptomics studies.
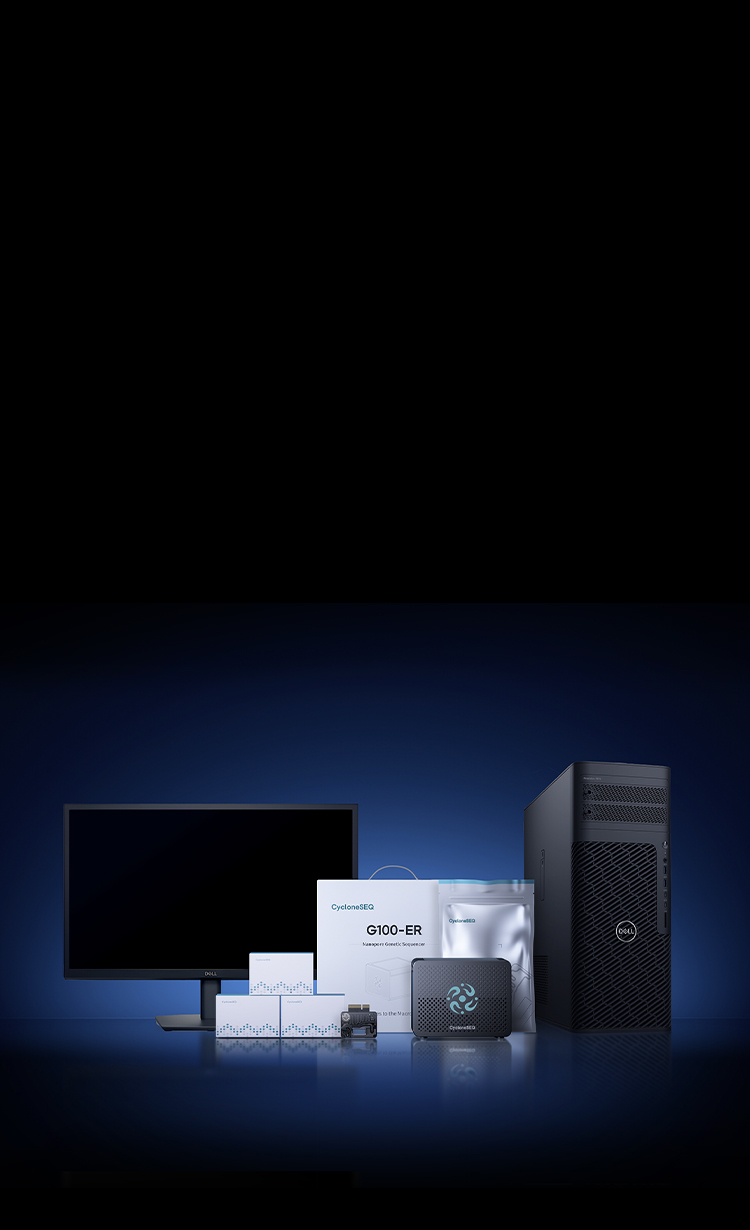






CycloneSEQ: a comprehensive sequencing tool solutionIntegrating sample preparation, nanopore sequencing, and data analysis and reporting, along with in-house developed reagents, consumables, and sequencers.Providing a one-stop, full-process sequencing solution to meet the needs of various application scenarios.

CycloneSEQ®BGI Hangzhou CycloneSEQ Technology Limited Company (abbreviated as CycloneSEQ®) is dedicated to promoting nanopore single-molecule sequencing technology from the laboratory to the forefront of industrial applications through continuous innovation and relentless exploration. CycloneSEQ® aims to provide comprehensive, highly accurate, and efficient full-process tool solutions for researchers in the global life sciences and applied transformation fields. CycloneSEQ is a nanopore sequencing technology brand independently developed by BGI Group and launched in 2024. It integrates cutting-edge crossover technologies such as high-performance proteins, advanced functional materials, large-scale integrated circuit, precision MEMS structure manufacturing, and artificial intelligence algorithms to achieve ultra-long read, direct and real-time sequencing. CycloneSEQ supports a wide range of scientific research and clinical applications, including rapid pathogen detection, genetic disease screening, and chromosome-level complete genome assembly.